1.本文介绍
本文对libuv定位为 平台层接口 而不是很多博客写的 nodejs三个基石之一 在于笔者对于libuv在设计实现上得出,libuv大部分能力是platform提供的,是rely on的,将底层能力抽象
本文内容是将官网的 Design Overview 摘录,介绍自我定位,和架构设计
2.基本定位
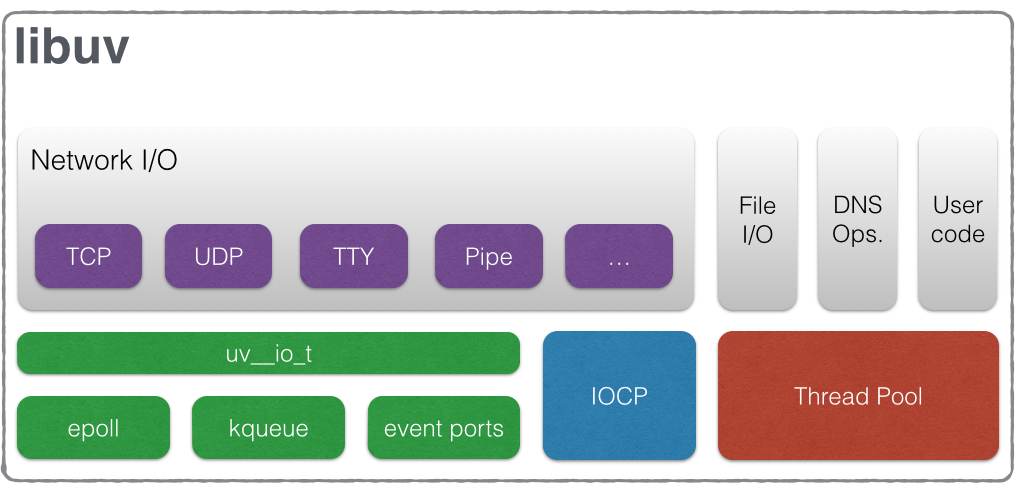
为nodejs而写的跨平台支持库,It’s designed around the event-driven asynchronous I/O model. 事件驱动的异步IO模型 (关键字:1. 为了跨平台:为上层提供统一能力接口 2. 事件驱动 3. 异步IO)
The library provides much more than a simple abstraction over different I/O polling mechanisms: ‘handles’ and ‘streams’ provide a high level abstraction for sockets and other entities; cross-platform file I/O and threading functionality is also provided, amongst other things. (高级抽象:贴近服务场景的能力接口:handles streams)
3.handle and requests
libuv provides users with 2 abstractions to work with, in combination with the event loop: handles and requests. (关键字:1. 用户使用的概念 与事件循环组合(与事件循环的概念关联) 2. 处理 和 请求(两种最基本行为的抽象))
Handles represent long-lived objects capable of performing certain operations while active. Some examples:
- A prepare handle gets its callback called once every loop iteration when active.
- A TCP server handle that gets its connection callback called every time there is a new connection.
Requests represent (typically) short-lived operations. These operations can be performed over a handle: write requests are used to write data on a handle; or standalone: getaddrinfo requests don’t need a handle they run directly on the loop.
handles:处理的主体,主动执行 request:处理的客体,执行行为本身
4.the I/O loop
The I/O (or event) loop is the central part of libuv. It establishes the content for all I/O operations, and it’s meant to be tied to a single thread. One can run multiple event loops as long as each runs in a different thread. The libuv event loop (or any other API involving the loop or handles, for that matter) is not thread-safe except where stated otherwise. (关键字:1. IO loop是内容是IO操作,并将IO操作和loop绑定的线程绑定 2. 一个loop一个不同的线程 3. loop handle 相关的api 调用都不是线程安全的)
The event loop follows the rather usual single threaded asynchronous I/O approach: all (network) I/O is performed on non-blocking sockets which are polled using the best mechanism available on the given platform: epoll on Linux, kqueue on OSX and other BSDs, event ports on SunOS and IOCP on Windows. As part of a loop iteration the loop will block waiting for I/O activity on sockets which have been added to the poller and callbacks will be fired indicating socket conditions (readable, writable hangup) so handles can read, write or perform the desired I/O operation. (关键字:单线程异步IO方法:poll一个non-blocking socket)
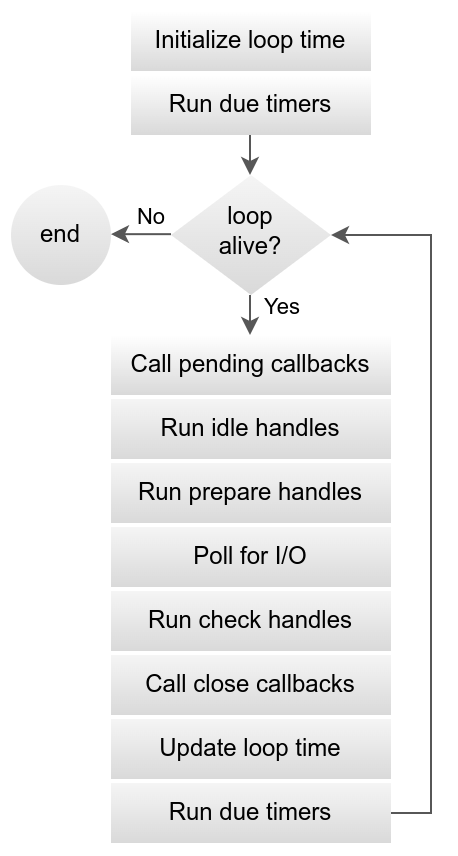
loop 循环迭代 流程图
libuv uses a thread pool to make asynchronous file I/O operations possible, but network I/O is always performed in a single thread, each loop’s thread.
异步文件I/O:线程池 异步网络I/O:总是在单线程执行:应为可以说网络IO本身就是“异步”的,发起执行的只是一个“守护线程”
5. File I/O
Unlike network I/O, there are no platform-specific file I/O primitives libuv could rely on, so the current approach is to run blocking file I/O operations in a thread pool.(关键字:文件IO是:在线程池执行的blocking I/O操作)
总结摘要
干了三件事:
- 统一接口:跨平台,贴近人文抽象,
- 线程池将阻塞文件I/O模拟为异步
- 使用loop和队列 打造事件驱动模型
实现目标:跨平台的异步IO事件驱动模型